
in this article i will show you full google search operators Google search operators can be extremely useful: They can help you find what you’re looking for faster on Google and can help you with many tasks related to SEO and content marketing.
The problem is:
Very few search operators are generally known. And even if you already know some operators, you may not get the most out of them .
What’s more:
Most of the articles, lists, and tables that already exist on the subject are outdated and contain many operators that no longer work.
Not so in this post:
I personally checked every single one of the 48 search operators in my list for you .
I have also put together 24 easy-to-implement examples below that can save you a lot of time in content marketing and SEO.
Table of contents
- 1. What are search operators?
- 2. Basic Search Operators
- 3. Search certain parts of websites
- 4. Other search operators
- 5. Search operators that no longer work (well).
- 6. OnPage-SEO (Example 1 – 9)
- 7. Promotion and Link Building (Example 10 – 18)
- 8. Other tricks and hacks (Example 19 – 24)
- 9.FAQs
1. What are search operators?
Strictly speaking , search operators are a relic of the past. From the times when Google couldn’t deliver results that were as precise as they are today.
These are special characters, Boolean operators or words followed by a colon, which are entered in Google together with a search term (single word or phrase) in order to specify the search queries.
Unfortunately, numerous search operators have been abolished by Google in recent years, such as B. The tilde (~) in 2013.
On the one hand, this has to do with the fact that the search engine algorithm is becoming more and more intelligent and the need for operators is no longer so great. On the other hand, certain search functions were deactivated, such as the Google blog search in 2011, which also meant the end for many operators.
You can find an overview of all the operators that no longer work in Section 5. But let’s start with the ones that still work.
2. Basic Search Operators
Here you can find all basic search operators, which are either boolean operators or consist of only one special character:
| search operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| “search term” | The quotation marks will only show you pages that contain your keyword in the exact spelling. | “walt disney” (this way you will only see results for the founder of Disney instead of the company) |
| OR or | | If you want to see results for two different terms at the same time, use this search operator. Instead of “OR” you can also use the pipe operator “|”. | Darth Vader OR Darth Maul |
| AND | Returns pages containing both keywords. Since Google returns results for both terms even without AND, this operator only makes sense in conjunction with others. | Darth Vader AND Darth Maul |
| – | With the minus you can specifically exclude a term so as not to steer the search query in the wrong direction. This makes sense especially when several terms are closely linked. | George Lucas -“star wars” (should you be looking for another non-star wars george lucas)George Lucas -“star wars” -lucasfilm -director (this is how you additionally exclude director and Lucasfilm to get even better results) |
| * | Can be used as a placeholder anywhere. | Crepes with* (to find out which fillings or side dishes you can eat crepes with) |
| () | The two brackets can be used to group search terms and link them to another search term. This makes sense if you want to display two or more general terms only in relation to exactly one topic. OR / AND are usually used within the brackets. | (Ewan McGregor OR Alec Guinness) Obi Wan Kenobi (this will show you all search results from both actors that relate solely to their role as Obi Wan Kenobi) |
| $ or € | With the dollar or euro sign, a price-related search can be carried out. | Star Wars Lego Millennium Falcon € (this will only show you search results associated with a price for the Millennium Falcon) |
| _ | An underscore makes it easier to control auto-completion on Google, as it acts as a placeholder at the desired position. | darth_ star wars (this is how all Sith Lords would be listed by Google Autocomplete, such as Darth Vader or Darth Maul) |
| #..# | This operator can be used to narrow the search to a specific time period or numeric range. | star wars movies 2000..2020 (shows only the movies from 2000 to 2020) |
3. Search certain parts of websites
Here you will find advanced Google search operators that allow you to search specific parts of web pages (such as anchor texts, URLs, the text or the titles) for words or phrases.
This is useful to make search results even more relevant to the entered keyword or to find pages optimized for a specific keyword:
| search operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| inanchor: | Shows only pages that link to another page with specific anchor text. | inanchor:mcgregor (only shows pages that contain a link with mcgregor in the anchor text )inanchor:mcgregor star wars (shows only pages that contain a link that contains mcgregor in the anchor text and is relevant to Star Wars) |
| allinanchor: | Works like inanchor: except that all words in the anchor text must appear (but not in the exact order). | allinanchor:mcgregor star wars (shows only pages that contain a link that has mcgregor , star , and wars in its anchor text ) |
| text: | Shows only pages that contain a specific word in the text. | intext:mcgregor (only shows pages that contain mcgregor in the text)intext:mcgregor star wars (only shows pages that contain mcgregor in the title and are relevant to Star Wars) |
| all text: | Works like intext: except that all words must appear in the text (but not in the exact order). | allintext:mcgregor star wars (only displays pages that contain the words mcgregor , star and wars in the text) |
| intitle: | Shows only pages that contain a specific word in the title. | intitle:mcgregor (only shows pages that contain mcgregor in the title)intitle:mcgregor star wars (only shows pages that contain mcgregor in the title and are relevant to Star Wars) |
| all intitle: | Works like intitle: except that all words must appear in the title (but not in the exact order). Unfortunately , allintitle: doesn’t work well in combination with many other operators. | allintitle:mcgregor star wars (displays only pages that contain the words mcgregor , star , and wars in the title) |
| inurl: | Shows only pages that contain a specific word in the URL. | inurl:mcgregor (only shows pages that contain mcgregor in the text)inurl:mcgregor star wars (only shows pages that contain mcgregor in the title and are relevant to Star Wars) |
| allinurl: | Works like inurl: except that all words must appear in the title (but not in the exact order). | allinurl:mcgregor star wars (only shows pages that have the words mcgregor , star and wars in the URL) |
4. Other search operators
| search operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| anus: | Displays pages with an update or publication date after a specified day or year. | m arvel after:2009-12-31 |
| around(x) | Shows pages that contain two keywords within a certain distance of each other. The x indicates how many other words can lie between the two keywords. | ewan mcgregor around(3) alec guinness (to find sites that mention ewan mcgregor and alec guinness very close together) |
| before: | Displays pages with an update or publication date earlier than a specified day or year. | marvel before:2008-12-31 |
| cache: | Shows the last cache of a website. | cache:disney.com |
| define: | This search operator displays the search term in the Google dictionary (in a box above the search). Only works for general terms. | define: disney |
| external: | Shows pages that have a specific file extension. | star wars ext:pdf |
| file type: | Displays pages with a specific file type. Can be combined with ext . | star wars file type:pdf |
| in | A converter within the search results. If you want to convert one unit of measurement to another, then you can use this operator. | 100 € in $ or 1000 m in km |
| imagesize: | With this operator you can limit the displayed images to a certain format in the Google image search. Is entered according to the scheme imagesize:widthxheight (in pixels). | star wars wallpaper imagesize:1920×1080 |
| location: | Shows only articles related to a specific location in Google News. | location:munich |
| maps: | With this operator you force Google to display map data for a search term. | map:hollywood |
| movies: | If you are looking for information about a film, then you can use this operator. If you have given permission for location determination, even showing times of nearby cinemas are displayed. | movie:black widow |
| related: | This operator helps you find pages or websites similar to the one you entered. However, this often only works for older or better-known websites. | related:starwars-union.com (Displays websites similar to the Star Wars Union fansite ) |
| site: | One of the most famous and important search operators that restricts the results to a specific domain. | site:projektstarwars.com (only one of the most well-known English-language Star Wars forums is searched) |
| sources: | You can use source: to restrict messages displayed within Google News to a specific source. | avengers source:tv spielfilm (only news about Avengers der TV Spielfilm are displayed here) |
| stock: | Displays stock information above search results. | stocks: disney |
| weather: | Displays the weather for a specific location above the search results. | weather:hollywood |
5. Search operators that no longer work (well).
Here you can find all Google search operators that have either been discontinued over time or no longer provide good results:
| search operator | Description | Set |
|---|---|---|
| @ | Adding @ in front of a word made it possible to search on social networks. However, the operator only brings mixed results. | unknown |
| ~ (tilde) | This operator was used to include synonyms of the search term in the results. | 2013 |
| # | This operator was originally introduced for Google+, but was abolished when the social network was discontinued. | 2019 |
| + | This operator was used to enable an exact search for a phrase or word. It had the same function as “search term”. | 2011 |
| blogurl: | Within the now discontinued Google blog search, you could use this operator to find all blogs that were managed under a specific domain. | 2011 |
| date range: | This operator showed pages published in a specific time period. | unknown |
| info: | This operator returned results with information about a specific page. | 2017 |
| location: | The aim of this operator was to provide you with local results for a search term. | unknown |
| inpostauthor: | Within the now discontinued Google blog search, this operator could be used to search specifically for articles by a specific author. | 2011 |
| allinpostauthor: | Similar to inpostauthor: . Here, however, the entire name was taken into account exactly. | 2011 |
| inposttitle: | Found posts within Google blog search that had specific words in the title. | 2011 |
| link: | The aim was to find pages that referred to a searched URL. Although it still delivers results today, these are often imprecise. | 2017 |
| phonebook: | You could use this operator to search for a person’s phone number. | 2010 |
6. OnPage-SEO (Example 1 – 9)
The first 9 examples are about on-page SEO.
For example how you can use Google search operators to find indexing problems and improve your internal linking:
1. Find out how many of your pages are indexed
The first step to find indexing problems is to enter the following search command on Google:
site:yourdomain.com
Here’s how you can see how many search results are in the index on Google:

This number shouldn’t be much higher than the number of your blog posts and/or pages. If you’ve written 100 blog articles but have 2,000 pages in the index, then you probably have a problem.
In short:
If you really want to know exactly how many of your pages are indexed, look in the Google Search Console. For a single page, you can also use the URL check in Google Search Console .
2. Check if affiliate links are indexed
Plugins like Pretty Links or Thirsty Affiliates are great for managing affiliate links or redirects and monitoring their performance.
However, if set incorrectly, they can be unnecessarily indexed (when incorrectly set as a 301 redirect instead of a 302 or 307 redirect).
You can find out if this is the case by typing the following into Google:
inurl:yourdomain.com/affiliate-praefix/
Note: Of course, this assumes that your plugin is set so that all your affiliate links have a prefix.
3. Find category and tag pages
WordPress category and tag pages do not belong in the Google index 90% of the time.
The reason for this is simple:
For the many topics and keywords, category and tag pages do not represent the best possible search results.
To find out whether your categories and tags have ended up in the index, first look in WordPress under Settings > Permalinks which category and keyword base you have chosen.
Then enter the following into Google:
site:yourdomain.com/category (replace category with your own category base if necessary) site:yourdomain.com/tag (replace tag with your own keyword base if necessary) site:yourdomain.com inurl:archive (finds archive pages on your website) site:yourdomain.com inurl:category (finds additional categories, e.g. of portfolio posts) site:yourdomain.com inurl:page (finds pagination pages on your website)
4. Find unwanted documents in the index (e.g. freebies)
There are some documents that you want to keep secret from your readers or that you uploaded to your website at some point and then forgot.
These include, for example:
- Materials from online courses
- paid e-books
- Freebies (which should actually only be available after subscribing to your newsletter.
- readme files
- company-internal PowerPoint presentations or PDF files
You can find such files with the following search command:
site:yourdomain.com (filetype:pdf | filetype:txt | filetype:ppt | filetype:xls)
Tip: You can also download some freebies from online gurus without having to subscribe to a newsletter somewhere. But don’t say you got that from me.
5. Examine your site for placeholder content
As a rule, you should definitely avoid content that is used more than once on different pages, because this can be seen by Google as duplicate content.
Really true:
The famous “Lorem ipsum” text or other placeholder content that you can create with a text generator or sample content like the “Hello World” post on WordPress is often forgotten to delete.
Even on reputable websites like the Encylopedia Britannica:
To find placeholder text on your website, you can use the following combination of operators:
site:yourdomain.com "Lorem ipsum"
You can find the example post created during the WordPress installation in the following two ways:
site:yourdomain.com "Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!" site:yourdomain.com "Hello World"
This is how you can find the example page created during installation in English:
site:yourdomain.com "Sample Page" site:yourdomain.com "This is an example page. It's different from a blog post because it will stay in one place and will show up in your site navigation"
And like this:
site:yourdomain.com "example page" site:yourdomain.com "This is an example page. It differs from posts because it always stays in the same place"
6. Finding duplicate content on your website
Google and users want to see unique content.
No run-of-the-mill texts that can be read anywhere or stolen from another website.
Online shops in particular often have a problem with so-called duplicate content.
Product descriptions or categories are often copied from other online shops or from the manufacturer.
Here’s an example (I didn’t have to look far for it):
I grabbed this article description of the Play Station from the Amazon:

And entered it into Google with the following combination of operators (you should exclude your own online shop from the search with the minus sign):
-site:yourdomain.com "text"

Over 50results.
That said, a great many people don’t put any effort into making their item descriptions unique…Tip: You can of course proceed in the same way to unmask other website operators who have copied your texts.
7. Check your website’s SSL status
When it comes to SEO, you should not only keep an eye on the competition, but also on your own website.
A very important point in your “OnPage Optimization” is the conversion of your website to HTTPs .
To determine whether Google has already indexed your entire website for the new URLs with HTTPS or whether you have even not yet switched parts of your website to HTTPS, you can simply use this search operator combination:
site:yoururl.com inurl:http
Or alternatively:
site:yourdomain.com -inurl:https
An investigation by Spiegel ONLINE shows, for example, that their senior portal has not switched to SSL.
8. Find out if your website has been hacked
If your website is hacked, 90% of the time it will be used to generate advertising revenue.
For this z. For example, all or part of your website may be redirected, or the hackers create hundreds or thousands of new pages that they try to get into the Google index. It may also be the case that advertising is simply injected into your existing pages.
In some cases, such a hack is unfortunately not obvious and can hurt your Google rankings if it goes unnoticed for too long.
To find out if your website has been hacked, the following search command can help:
site:yourdomain.com viagra OR porn OR casino OR dating OR insurance OR debt OR sex OR pharmacy OR poker OR "make money online" OR credit OR hacked
This is how you search your website for typical spam words (you can add more words to the command if you want).
IG Techh wasn’t hacked (thank goodness!):
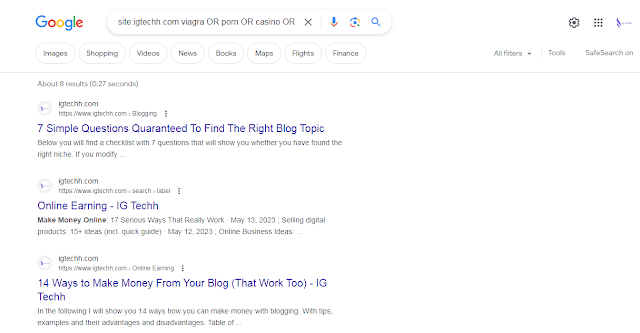

Note: The search command can also be used to find spam comments that you may have accidentally shared at some point.
9. Find internal linking opportunities
Internal links help your visitors find their way around your website and are an important building block for SEO.
However, once your website has reached a certain size, linkable content becomes harder to find…
How good that Google search operators can also help here!
I enter the following search command into Google every time I publish a new article:
site:yourdomain.com intext:keyword
You can intext:also omit it, which usually gives just as good results:
site:yourdomain.com keyword
Only pages of yourdomain.com that contain the specified keyword in the text (in my example “SEO”) are displayed:

7. Promotion and Link Building (Example 10 – 18)
In this section, I’ll show you 9 recipes to help you build links or find PR opportunities.
10. Find sites that accept guest posts
Guest posts are still a great source of backlinks and can also help you position yourself as an expert in a niche or get your blog known .
The problem is just:
Not every website also accepts guest posts.
This means that if you write to webmasters on the off chance that they will decline or not answer at all.
However, you can use a search operator to only show you sites in the SERPs that already have guest posts online on their site, which significantly increases the likelihood of a positive response.
We assume that guest contributions are also marked as such. This usually happens in the first sentence of the post, in which the author and his website are briefly introduced: This is a guest post by … who runs the website … .
So it makes sense to use the following command here:
your topic intext:guest post

Alternatively, you can also use the following searches:
your topic inurl:guest post yourtopic inurl:guest posts (for tags and category pages) yourtopic inurl:guestauthor (to find profile pages of guest authors) yourtopic inurl:guestauthor (to find profile pages of guest authors) your topic intext:guest author your topic intext:guest author your topic intitle:guest post
11. Find your own mentions
You can also use search operators to find out whether you, your website or your brand name was mentioned on a website.
Just use the following search command:
yourbrandname -site:yourdomain.com
And then only display the search results for the last month:

As in the screenshot above, you can also make other exclusions, e.g. B.Pinterest.
If your brand name is in a foreign language, it can also make sense to only show you pages in English .
Checking your mentions regularly can do the following:
- You can find people who like your brand and content and connect with them
- You can email people who mention your brand but don’t link to your site and ask them to amend a link (arguably the easiest link building method there is).
12. Find mentions of your competitors
Not only can it be useful to find your own mentions, but also those of your competitors.
Because where your competitors are mentioned, there is always potential for you to be mentioned instead or in addition.
The search command for this is a bit more extensive, but I’ll explain to you in a moment how all the search parameters interact:
(in text:"competitor1" OR "competitor2") -site:competitor1.com -site:competitor2.com
Here’s an example using IG Techh competitors:
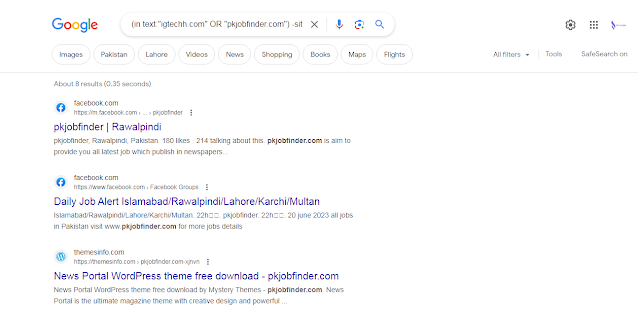
And here is the explanation:
- Searches
intext:specifically for websites that mention your competitor 1 or your competitor 2 in the text. - With the
ORoperator, you deal with two competitors in just one search, which saves time (you can also add a third or fourth if you want) - With
-site:you exclude the own websites of the competitors. Otherwise, Google would present you with many results coming from their websites.
Actually simple, right?
13. Find commenting opportunities
Blog comments are a great way to get in touch with other influencers or bloggers in your niche and thus increase your own awareness.
To find related blog articles that allow comments, you can use this search command:
your topic "save comment"

I recommend you to test more variations because the button labels are not the same everywhere:
- Send/Leave Comment
- Send/send/send comment
- Leave/Write a comment
- Save my name, email and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
14. Find cooperation partners
If you are a blogger, it is essential to network and collaborate with other bloggers in your niche. Be it to exchange knowledge, to recommend each other or to start a joint venture.
To find other blogs in your niche, just type the following into Google:
your topic inurl:blog
So you get e.g. B. in no time a long list of sewing blogs:

15. Find round-up posts
A simple way to make your blog better known is through so-called “round-up posts”.
These are posts in which a blogger introduces other bloggers or collects expert opinions on a specific topic.
You can do this e.g. B. with a search command according to the following scheme:
intitle:your-topic blogs inurl:your-topic-blogs

Or alternatively:
intitle:bloggertype inurl:bloggertype:
16. Find infographics
Infographics may not be as “hip” as they were a few years ago…
But it can still be worth creating your own infographics and then contacting bloggers or online magazines and asking them to include them. Be it for link building or increasing your own awareness.
Which greatly increases your chance of a positive response:
Only contact bloggers or online magazines that already have infographics embedded on their website.
Because with them it is more likely that they “have an open ear” for your request.
And you can find that out with the following search command:
yourtopic intitle:infographic inurl:infographic
For example, IG Techh could create an SEO infographic and contact t3n or OnlineMarketing.com for distribution:

Tip: To further increase your chances of success, you can also work with a date filter and only display search results from the last 6 – 12 months.
17. Find collections of links
Link collections like this one on the subject of GDPR are great for link building.
If you have a great and thematically relevant article on the subject of GDPR yourself, simply ask the website operator to include your link.
Easy.
You can find link collections with the following search commands:
your topic intitle:"useful links" your topic intitle:link collection your topic intitle: resources
18. Check backlinks of a domain
Finding out which websites linked you or one of your competitors does not always have to be a backlink checker.
Even though the operator link:has officially been discontinued, it still gives some results:

To get better results, you should exclude social networks and the domain to be examined from the search, like this:
link:domain.com -site:domain.com -pinterest -facebook -twitter -linkedin -xing
Since the domain name often appears in the anchor text, you will also find many backlinks with the following search parameters:
"domain.com" -site:domain.com -pinterest -facebook -twitter -linkedin -xing
8. Other tricks and hacks (Example 19 – 24)
The benefits of search operators go far beyond link building and PR.
Below I have put together a few more recipes that can help you in your online business or with internet research:
19. Find cooperation partners for sponsored posts
I can tell you from my own experience:
Getting a business to partner with you on a sponsored post is easier if the business has worked with bloggers in the past.
And to find such companies, Google search operators can help you!
I’ve found the easiest way to find Sponsored Posts is through WordPress categories and tags . Because many bloggers create their own categories and/or tags for sponsored posts:
your topic inurl:category/sponsored your topic inurl:tag/sponsored your topic inurl:category/werbung your topic inurl:tag/advertising your topic inurl:category/cooperations

blog brand name (inurl:sponsored | inurl:ad | inurl:ad) blog product category (inurl:sponsored | inurl:ad | inurl:ad) blog product name (inurl:sponsored | inurl:ad | inurl:ad)

Google will show pages that contain the word “blog” and the product category (or product name or brand name) and have either sponsored , advertising , or ad in the URL.
20. Find subdomains
You want to know which subdomains there are for a domain and what content can be found there?
Then you can use this search operator:
site:*.domain.com -inurl:www
Or alternatively:
site:*.domain.com -https://domain.com
21. Find social media profiles
You want to address a blogger or influencer in your niche (e.g. for the purpose of a collaboration)?
Then it is often easiest to do it via social media.
You can find the social media profiles of a specific person e.g. B. by entering the following combination:
Name (site:facebook.com | site:twitter.com | site:linkedin.com | site:instagram.com | site:xing.com)
22. Browse question and answer portals
Question and answer portals such as Quora or Gutefrage.net are a popular method for building initial backlinks quickly and effectively.
But they can also be very helpful to get a feeling for your own target group and their problems and goals.
The problem:
Quora and Gutefrage.net are huge websites with hundreds of thousands of subpages.
It can be difficult to find specific topics. Especially since their internal search functions are not particularly good.
To get results faster, you can use the following combination of operators on Google:
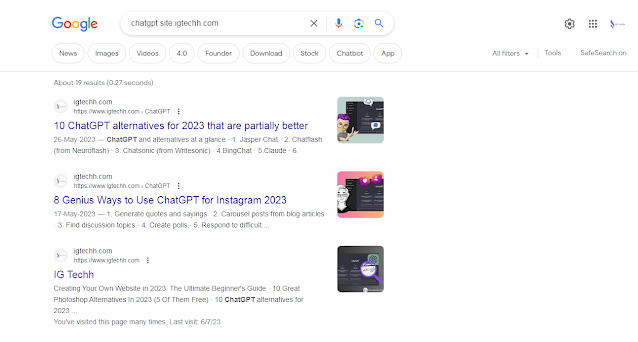
site:domain.com intitle:"your topic"
That’s it.
So you can z. B. Display search results from igtechh.com that deal with the topic of WordPress:
If you intend to comment in threads and possibly place a link to your website, it is advisable to use the search filter to set the search results to last month or even better last week :

It always looks a bit suspicious when someone comments on a thread that is several months or years old…
If you don’t get good results, you can also experiment with the following search commands:
site:gutefrage.net inurl:your-topic site:gutefrage.net your topic site:gutefrage.net "your topic"
23. Find forum threads on a topic
Forums are very good for getting to know your own target group better. Because they depict their challenges, problems, but also expectations and wishes on a specific topic.
You can use the following combination of operators to immediately find suitable forum threads:
your topic inurl:forum

To prevent this, you can include URL snippets typical of forum threads:
yourtopic inurl:forum AND (inurl:topic | inurl:view | inurl:thread)
24. Restrict search results to specific TLDs
If you are looking for link building or promotion opportunities, or if you want to refine your internet research, you can also limit your search to specific TLDs (top-level domains, i.e. .com, .net or .org).
For this you enter:
yourtopic site:.tld
So you can start your search e.g. B. Restrict to university and educational organizations:
Or on Google’s own blogs and websites:

9.FAQs
Here are answers to common questions about Google search operators:
What advanced search options does Google still have?
First, there’s Advanced Search on Google, which you can access from the Settings menu above the search results:
Secondly, there are the search filters, with which you can search for e.g. B. can limit time:
Thirdly, there is the possibility to change the URL of a Google search directly:
For example , by appending &psw=0 to a Google search, you can B. switch off the fact that personalized search results are displayed to you.
You can find an overview of such URL modifiers at MOZ .
Do the Google search operators also work for image searches?
Unfortunately, most of the search operators listed do not work for image searches. However, you can use imagesize:widthxheight to display only images of a specific format.
